Digital Assets
Digital Assets
1. Forecast market development for digital assets
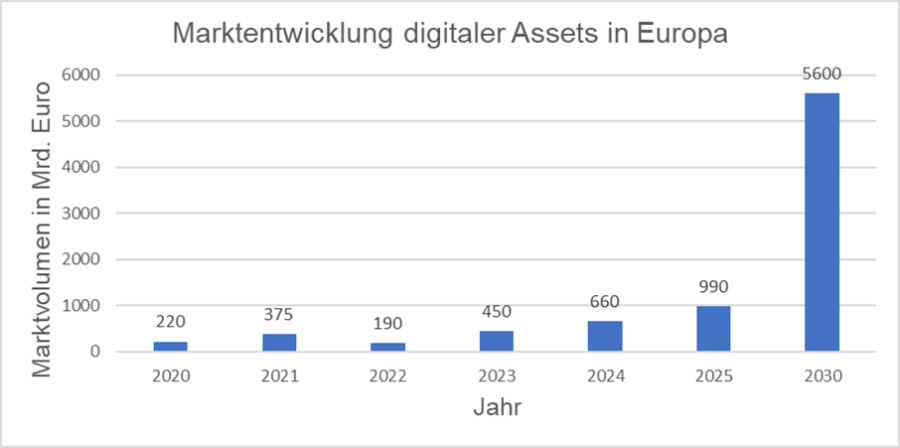
According to a forecast by Statista, the market for digital assets in Europe will reach a volume of around 1 trillion euros in 2025 and will increase more than fivefold in the following five years.
The market development is currently slowed down due to the lack of standardization and the fragmentation of the market. Existing solutions often only cover certain types of assets or use cases and integration into existing investment processes, IT and business infrastructure, is often not yet the focus. In addition, not all areas relevant to digital assets are yet regulated.
With the filling of regulatory gaps, which leads to greater legal certainty, the consolidation of providers and the standardization of technologies, economies of scale are expected to be increasingly achieved in order to significantly accelerate the dynamics in the coming years.
Surveys, e.g. by Laser Digital (Nomura Group) or Fidelity Digital Assets, also confirm the strong interest of professional investors in investing in digital assets and diversifying their investments.
2. Legal Framework
The development of the digital assets market is supported by the creation of a regulatory framework. This steers the market in an orderly manner and ensures legal certainty and planning for market participants.
There are various motivations for regulating the digital assets market. The most important include:
- Promoting the competitiveness of the digital industry in Europe
- Creating a framework for new services
- Reduce barriers to digitalization
- Establish legal certainty and trust regarding digital assets
- Promote investments in digital technologies (especially in the distributed ledger area)
- Create alternative financing options for companies
- Ensure stability of the crypto market
- Investor protection.
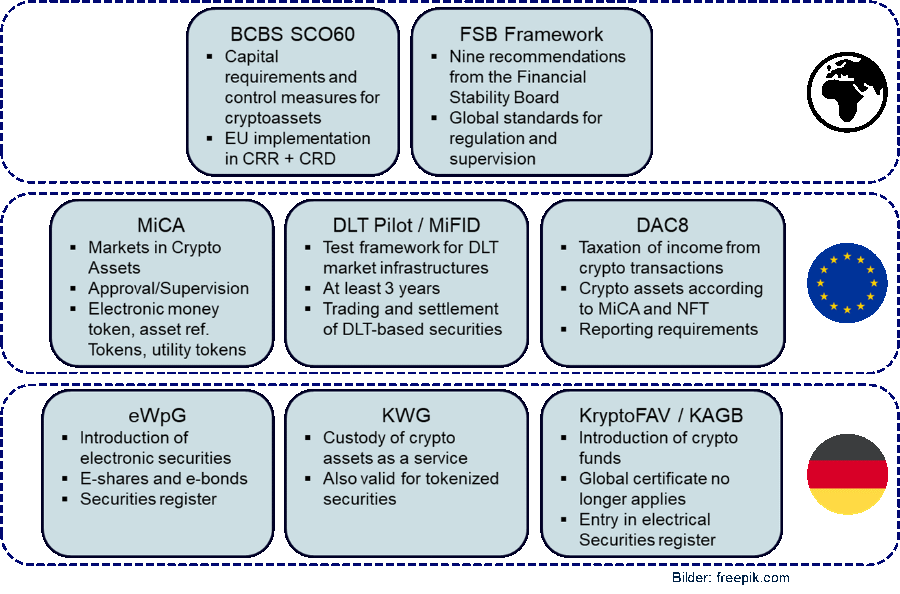
The following graphic shows an excerpt of the regulatory requirements that have already been introduced and are planned in relation to digital assets:
The next milestone on the subject of digital assets in Germany is the introduction of e-shares in the eWpG through the adoption of the Future Financing Act (ZuFinG) in November 2023. This improves the previously established electronic bonds and crypto funds framework.
The state of the art for implementing crypto securities is digital ledger technology (DLT) and blockchains in particular, although the eWpG is fundamentally formulated in a neutral manner open to all types of technologies.
Regulatory requirements and recommendations basically exist on three levels: Global, EU and Germany.
Global agreements are usually not immediately binding and are first implemented into EU law (like BCBS SCO60) or, like the Financial Stability Board Framework, they are recommendations to the relevant regulators.
At the European level, the above-mentioned Markets in Crypto Assets (MiCA) regulation, which will come into force in 2023, is of particular importance. As a European regulation, MiCA applies directly in the member states, so it does not require prior implementation by the individual member states. This is intended to achieve the highest level of harmonization.
The German legislator has created the legal framework for the securities and funds not covered by MiCA with the eWpG and KryptoFAV.
The following figure provides an overview of the most important regulatory requirements:
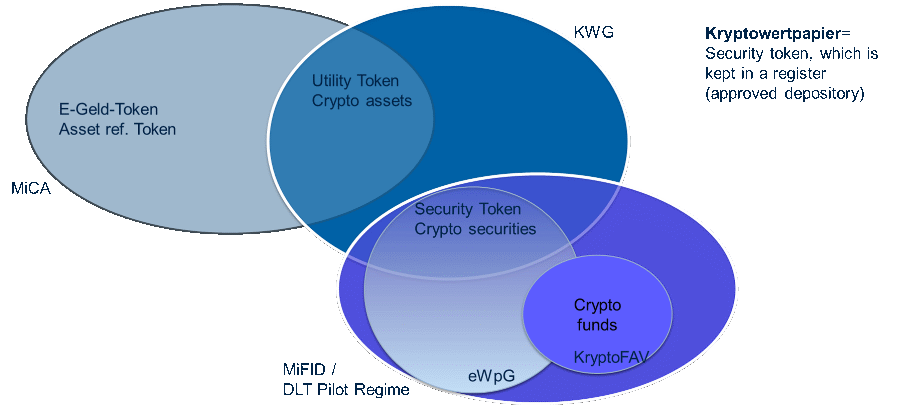
The following types of digital assets can be broadly differentiated:
The EU regulation MiCA distinguishes between e-money tokens (e.g. stablecoins tied to an official currency such as the US dollar), asset-referenced tokens and utility tokens (often usage rights).
Securities and security tokens are excluded from MiCA; they continue to fall under MiFID. Non-fungible tokens (NFT) are also not subject to MiCA regulation.
Issuers must create a so-called white paper for new products and submit it to the responsible authority.
E-securities according to eWpG represent a special category of security tokens. These are equivalent to traditional securities and allow for the waiver of physical securitization.
3. Applications in practice
The following table provides an overview of available applications for trading, settlement and custody of digital assets..
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| SWIAT |
Stands for “Secure Worldwide Interbank Asset Transfer”. The Deka subsidiary SWIAT is a blockchain-based platform for cross-border settlement of securities in real time. Solutions offered by SWIAT are:
|
| Smart Derivative Contract |
In a pilot project in 2021, an OTC interest rate derivative was traded in the form of a digital smart derivative contract (“SDC”) and the settlement was processed via Deutsche Börse. DZ Bank and BayernLB were involved. A similar test transaction was carried out in 2022 between DZ Bank and Union Investment, this time with the participation of an asset manager, for an interest rate swap as a Smart Derivative Contract (SDC). The resulting payments were carried out in real time using a settlement token, a digital account management system, via SEPA payment transactions. |
| SettleMint |
SettleMint was founded in Leuven, Belgium in 2016. SettleMint is a cross-industry low-code platform for developing blockchain applications. In the context of finance and asset management, SettleMint also offers the possibility of tokenizing real assets. The tokenized assets can then be traded on the platform. |
| Fundsonchain |
Fundsonchain GmbH is a start-up company based in Saarbrücken. With the fundsonchain platform, it is possible to develop a fully digitalized processing of investment funds and also to create new forms of digital fund distribution. The platform enables fully digitalized fund processing of tokenized fund shares based on distributed ledger technology (DLT). |
| SWIFT Tokenized Assets | SWIFT conducted a series of experiments with financial partners and market infrastructure providers to enable the global exchange of tokenized assets via its infrastructure. The aim is to link digital central bank money (CBDCs) with digital assets and existing and new payment systems. |
| D7 Deutsche Börse |
D7 is a digital issuance platform from Deutsche Börse, which covers not only the issue of digital assets but also post-trading (settlement and custody). The platform is purely digital, i.e. securities must be digital or tokenized, but it offers the possibility to connect with other platforms. D7 consists of the following components:
|
| Enzyme |
Enzyme Finance is an Ethereum blockchain-based protocol and platform for decentralized asset management (DeFi). Enzyme aims to simplify the access to asset management for investors, removing restrictions, waiving a minimum investment amount or high management fees. Investors can enter their risk profile, which filters out unsuitable risk profiles and investment strategies. In addition, they can exchange ideas with other users about investment strategies, manage their own portfolios or invest in other users’ funds. |
| UI Enlyte | Enlyte is a FinTech company founded in 2020 by Universal Investment. It offers an end-to-end investment platform with functionalities that institutional investors, fund initiators and asset managers need to facilitate ordering, trading, execution and custody of digital assets. |
| DZ Bank Digitalverwahr-plattform |
With a volume of over EUR 300 billion, the cooperative DZ Bank is currently the third largest depository in Germany and the largest depository based in Germany. In 2022, the bank began building a blockchain-based digital custody platform for institutional customers. Here, crypto securities are initially taken into custody in accordance with the eWpG, such as a crypto bond from Siemens, which Union Investment and DZ Bank had previously subscribed to. In addition, DZ Bank has applied for a crypto custody license from BaFin in order to be able to store cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin for institutional customers in the future. In addition, the circle of customers is to be expanded from institutional customers to private customers. This is to be implemented in cooperation with the IT service provider Atruvia. |
Table 1: Overview of applications related to digital assets
4. Anadeo Theses
The question for asset managers is what this means for front-to-back processes, what advantages the new technologies offer, and how a high level of automation can be achieved here.
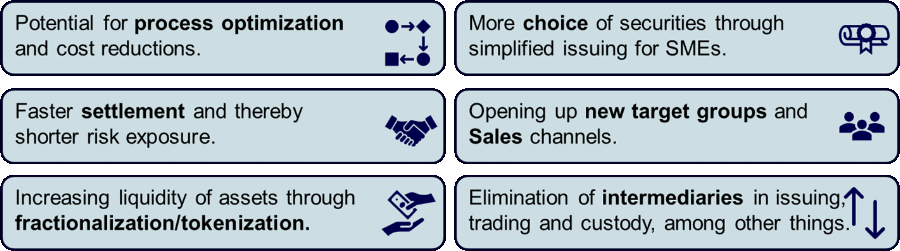
The potential of the new technologies and processes includes:
We have identified a need for significant adjustments in the front office, middle office and back office space, whereby the adjustments should be tailored to the individual investment process and specific requirements. We would be happy to discuss these with you if you are interested.
Anadeo derives the following theses from the previous argument:
- Thesis 1: We assume that a hybrid approach will be pursued in the next few years because traditional assets will continue to be needed for many years to come. This requires the integration of digital assets into existing investment processes, which must be done individually for the requirements of the asset managers.
- Thesis 2: The volume of digital assets will grow rapidly, so scalability and process automation are of great importance.
- Thesis 3: In order to benefit from the growing market for digital assets and remain competitive, asset managers should now set the course for integrating digital assets into their own processes.
- Thesis 4: The new technology offers the possibility of optimizing the process of providing collateral.
5. Anadeo Services
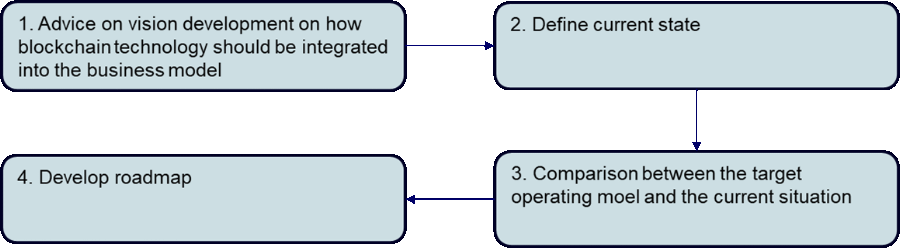
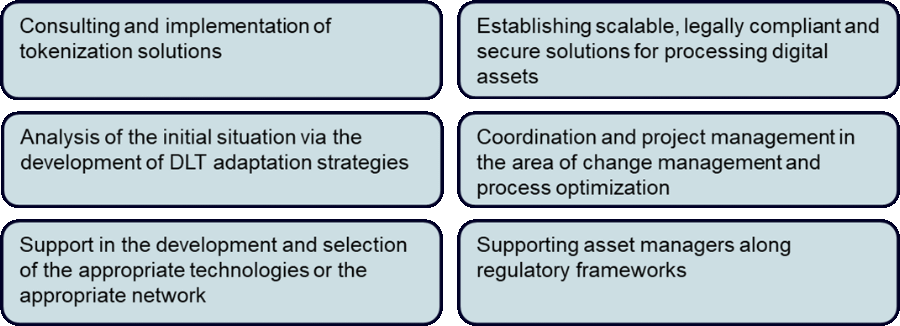
The following figures show a possible approach to integrating blockchain technologies into current business models and the services offered by Anadeo in this context.
To discuss the topic of digital assets or projects in this environment with us, please send an email to info@anadeo.com or call +49 6196 7694770
6. Credentials
Anadeo has already worked on various projects in the areas of regulation, interfaces, processes, automation and GAP analyses.
An outstanding project included the in-house development of complete Solvency II reporting for securities, for which Anadeo took over project planning, organization and coordination of business analysts and developers. In another project, the technical implementation related to the improvement of several export interfaces in SimCorp Dimension to load the reporting data warehouse was realized. Anadeo also led the implementation of a new portfolio management system with master data, including connecting a new data source to Markit EDM DWH, developing master tables and data quality and consistency checks. Other projects included the technical and procedural optimization of limit controlling, the configuration of the SCD and the implementation of Aladdin Front and Middle Office including interfaces and processes. In 2014-2015, the focus was on optimizing system performance in the SCD area and redesigning fund accounting processes. During 2016-2017, Anadeo led the proof of concept for Aladdin Accounting as the sole IBOR. For various RFI/RFP projects for compliance software, including MADII MAR, COI and PRIIPs, Anadeo provided project management for the project set-up, RFI/RFP documents, business and IT requirements, and provider response -Queries. It is worth noting that in one of the projects no new software was selected, but the existing one was adapted and enhanced with the implementation of additional modules.
Make-or-Buy analysis of securities master data (2022/2023)
In the project, the requirements for the central master data system were determined based on interviews with stakeholders. The requirements were then prioritized (according to the MoSCoW system) and the effort was estimated. Based on the estimated and prioritized requirements, a fundamental decision (make-or-buy) was prepared.